ISO 13485 is the internationally recognized quality management benchmark for medical device manufacturers. The ‘ISO’ in ISO 13485 stands for the International Organization for Standardization, which publishes the international standards governing most modern industries. Getting ISO 13485 certified guarantees the trust of regulators, stakeholders, and future customers while quickening route to market with ISO1345 compliance. ISO 13485 is an internationally agreed upon set of standard quality management system (QMS) requirements for any company involved in the design, production, installation, servicing and manufacturing of medical devices. ISO 13485 was published in 1996 with revisions in 2003 and 2016. The current version, ISO 13485:2016, came into effect in March 2016. The goal of these requirements is to ensure that medical devices and services consistently meet customer expectations and relevant regulatory requirements.
ISO 13485 certification vs accreditation
ISO 13485 certification is provided to any medical device organization meeting the requirements of ISO 13485. ISO accreditation, on the other hand, is provided to a conformity assessment body as proof of its integrity, impartiality and operational ability. A testing lab, certification body, or inspection agency needs accreditation. The companies that those bodies inspect for compliance get certified once they pass their audits.
ISO is an international non-governmental organization of industry leaders who share their knowledge and expertise to provide solutions for global challenges. ISO 13485 effectively covers ISO 9001 with a few additional requirements. Consumers and the life science supply chain have come to trust ISO, and they’ll often refuse to purchase medical device products from companies that lack ISO 13485 certification. To obtain CE marking—which indicates conformity with safety standards for products sold in the European Economic Area—medical device manufacturers must get ISO 13485 certified with a notified body and have a quality management system in place.
FDA plans to harmonize its own 21 CFR 820 medical device quality requirements with those of ISO 13485. The FDA’s new QMSR may be launched in 2026 – making ISO 13485 best practice a key part of American national regulatory expectations.
ISO 13485 certification cost
ISO 13485 certification cost varies significantly depending on the size and complexity of the organization and product offering. Fees are paid directly to the notified body conducting the ISO 13485 assessment. Approximately $20,000 is the minimum. This comprises the typical annual certification fee of $3000-5000, typical audit costs of around $3000 per day, billable planning and reporting time, and the associated work and time expenses preparation work.
ISO 13485 Elements
ISO 13485 includes requirements for design and development, risk management, production and post-production processes for medical device companies. ISO 13485 key certification requirements:
1. Quality management system (QMS)
To be certified to ISO 13485, a company must implement and maintain a quality management system meeting the requirements set out in the standard. According to ISO, organizations need to:
- Determine the processes the quality management system requires and what’s needed to apply these processes throughout the organization, taking into consideration the various roles involved.
- Apply a risk-based approach to the control of the appropriate processes needed for the quality management system.
- Determine the sequence and interaction of these processes.
2. Management responsibility
Management should provide evidence of its commitment to the development and maintenance of the quality management system and its effectiveness by exhibiting:
- Communicate the importance of meeting regulatory requirements.
- Establish a high value quality policy.
- Ensure that quality objectives are established.
- Conduct management reviews.
- Ensure availability of quality management system resources.
3. Resource management
To meet major regulatory and customer requirements, resources need to include:
- The provision of resources.
- Human resources.
- Infrastructure.
- Work environment.
- Contamination control.
4. Product realization
ISO 13485 Section 7.1 requires appropriate planning:
- Establish the quality requirements for the product(s).
- Define what your required processes will be and what supporting documentation will be needed for those processes.
- Outline the company infrastructure that will need to be created and what the work environment should be like.
- Define employee qualification and training requirements.
- Establish your processes for verification, validation, measurement, monitoring, handling, inspection, storage, distribution, and traceability.
- Organize all of the information so it can be easily accessed and understood.
5. Measurement, analysis, and improvement
According to ISO, “the organization shall plan and implement the monitor, measurement, analysis, and improvement processes” related to the quality management system and products and needs to:
- Demonstrate conformity of product.
- Ensure conformity of the quality management system.
- Maintain the effectiveness of the quality management system.
ISO 13485 diagram of the key QMS activities:
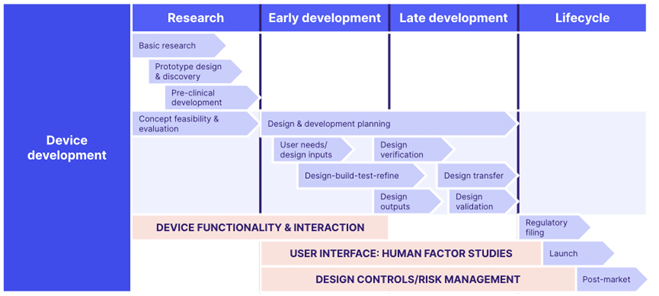
ISO 13485 contains 8 clauses as part of its requirements:
- Scope
- Normative References
- Terms and Definitions
- General requirements
- Management responsibility
- Resource management
- Product realization
- Measurement, analysis and improvement
Meaning of each clause:
1. Scope
The scope sets out the intended outcomes of the modern medical device quality management system, including the significance of the process approach and continuous improvement.
2. Normative References
Provides details of the reference standards or publications relevant to the standard, including ISO 9001:2015.
3. Terms & Definitions
Details terms and definitions applicable to the standard, including definitions of Active Implantable Medical Device, Active Medical Device, Advisory Notice, Customer Complaint, Implantable Medical Device, Labeling, Medical Device and Sterile Medical Device.
4. General requirements
Lays out the broad requirements for a properly documented ISO13485 QMS, including:
- Quality manual with clear QMS scope.
- Documentation control procedures.
- Required forms, records, and SOPs.
5. Management responsibility
Concerns the role of ‘top management’: the group of people who direct and control your organization at the highest level. Customer and patient satisfaction and safety should be overseen and maintained by top management with:
- Clear responsibilities.
- Frequent management reviews.
- A clear quality policy with objectives.
6. Resource management
Requirements for how resources are managed and applied to meet your quality objectives, including personnel, equipment and training.
7. Product realization
Maps out requirements for the end-to-end medical device product realization process, including:
- Production and manufacture.
- Capturing and actioning feedback.
- Planning.
- Design.
- Purchasing.
- Traceability.
8. Measurement, analysis, and improvement
Breaks down how to monitor and analyze your processes with a view to continuous refinement and improvement including:
- Auditing.
- CAPAs.
- Non-conformance control.
- Measuring and maximizing customer satisfaction and patient/product safety.
ISO 13485 vs. ISO 9001
ISO 9001 lays the framework for a quality management system that can be applied no matter what industry you’re in or what the product, service, or company size is. A manufacturer of medical devices needs to seek ISO 13485 certification. The key difference between ISO 13485 and ISO 9001 is focus. ISO 9001 is broad and can be applied to any business. ISO 13485 is niche, and it is designed specifically for medical device companies. ISO 13485 therefore has additional requirements not found in ISO 9001, that are specific to medical device manufacturers.
Similarities between ISO 13485 and ISO 9001
- Each standard helps organizations achieve a quality management system.
- Both place a focus on risk mitigation and assessment.
- Both utilize the Deming cycle, also known as Plan Do Check Act
- They each place a focus on competency and infrastructure for quality.
- Both emphasize understanding the customer for the realization of quality products.
ISO 13485 Additional requirements
- Device master record explicitly defining QMS requirements.
- Feedback and review system for non-conformance detection 18.
- Product quality control (monitoring and measuring) throughout the production process.
- Set quality requirements must be met before product release and delivery.
- Advisory notices, rework activity, release of non-conforming product (which still meets regulatory requirements) must be documented.
- Personnel require access to procedures, requirements, and reference materials at the point of work.
- Unique and specific records for every approved and verified device batch.
- Installation and verification device requirements.
- Maintained records of device installation, verification, and servicing activities and procedures.
- QMS containing product specification documents and quality policy, with a framework for reviews and updates controlled by the management team.
- Management must verify QMS goals and compliance.
- Documented procedures for shelf life, quality data collection/analysis/ retention, maintenance activity, risk/environment management, adverse event flagging, product conformity, identification, returns, maintenance, labeling, and packaging.
ISO 13485 medical device file
The ISO 13485 medical device file (MDF) is a key document to demonstrate compliance to the standard. The MDF should document your device’s design, development, and testing activity to prove it works as intended. It should also include risk management activities, as well as any post-market surveillance data once the device is in the public.
Tips to prepare for ISO 13485 certification
- Familiarize yourself with the guidelines.
- Take time to read the guidelines thoroughly and make sure you understand what’s required of you to become certified. You can view a preview and purchase the complete document on ISO13485 from ISO’s website.
- Meet CAPA standards.
- Refer to the FDA’s inspection guidelines and to ISO 13485 8.5.3 (prevention) and ISO 13485 8.5.2 (correction) to ensure your company meets CAPA standards. Failure to meet CAPA standards is the number one trigger for FDA citations in the medical device industry.
- Implement complaint procedures.
- Establish complaint procedures that follow the guidelines laid out in FDA CFR 820.198 and ISO 13485 8.2.2. A lack of standard procedures for handling complaints or failure to provide evidence that they followed procedures is the second most common reason organizations received a 483 observation.
- Include purchasing controls
- Create a written procedure for supply chain management to reduce the risk of noncompliance or supplier risks that could compromise the device quality.
- Develop MDR procedures.
- MDR (Medical Device Reporting) should include events and annual reports as detailed under FDA CFR 803.17 and ISO 13485:2016. Written procedures and systems are critical for compliance with record-keeping guidelines for MDR.
- Create a process to prepare for the audit.
- Review the following areas every three months:
- Design
- Trainings
- Purchasing
- Quality assurance
- Focus on upstream quality (UQA) which means putting effort into planning in the early stages to reduce quality issues later down the line.
- Prepare for audits.
- Use an eQMS, not a paper-based system to provide essential functions such as document control, training, and the ability to expand to Corrective and Preventative Actions (CAPA).
Benefits of ISO 13485:2016 certification
Adhering to the guidelines set out in ISO 13485:2016, the benefits include:
- Bringing quality and continuous improvement into the medical device organization.
- Improved patient/customer satisfaction – by consistently providing safe medical devices that meet customer requirements.
- Enhanced reputation and credibility.
- Greater efficiency.
- Reduced costs.
- Improved risk management.
- A stronger foundation for growth.
ISO 13485 software
ISO 13485 software is a specific category of quality management software designed for medical device companies seeking ISO 13485 certification. Medical device quality management software offers a diverse range of business benefits, including centralizing document and design control information and allowing collaborative digital workflows for closing out CAPAs.
